Energy and Elements within a biological
system
Energy :
Does not cycle within a biological system, it is transferred from organism to
organism.
Energy
p Energy
passes through biological systems
n Energy
enters the system via photosynthesis
n Energy
passes through the biological system through trophic levels via metabolism
(cellular respiration)
n Energy
leaves the biological system in the form of heat.
Elements: cycle within biological systems
Element: Carbon
p Carbon
cycles through a biological system in both inorganic and organic compounds
p Photosynthesis
fixes inorganic carbon into an organic compound (glucose)
p Cellular
respiration converts organic carbon into inorganic carbon in the form of carbon
dioxide.
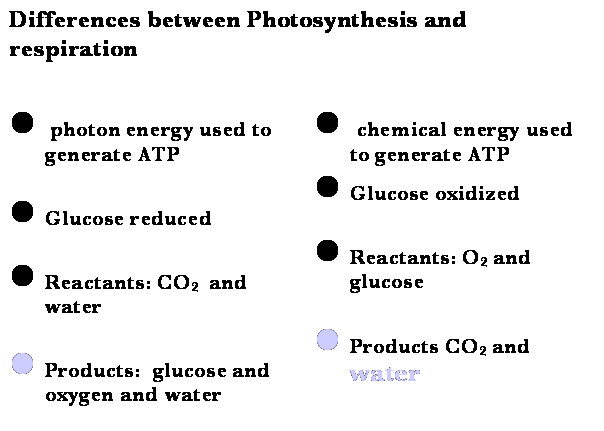
1st Law of thermodynamics
p Energy
can not be created or destroyed; it can only undergo conversion from one form
to another
pTherefore photosynthesis does not create energy
What is photosynthesis
p The
conversion of electromagnetic energy to chemical energy
pLight
photons supply the energy to remove the carbon from carbon dioxide and link
them together to form a compound of glucose.
light
6 CO2 + 6 H2O C6H12O6
+ 6 O2
Three phases to photosynthesis
p Sunlight
energy captured
p Using
sunlight energy to synthesize ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
p Using
ATP to synthesize organic compounds from carbon dioxide
(fixation
of inorganic carbon)
How plants capture electromagnetic energy
p Plant pigments absorb light energy
n chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, carotenoids
Where are the pigments located within a
plant cell?
light
6 CO2 + 6 H2O C6H12O6
+ 6 O2
p Light dependent
reactions -Thylakoid
pLight independent reactions - Stroma
Light dependent reactions
Photosystem II
p Requires H2O
§
Replaces
electrons oxidized
§ Produces O2
p H+ (proton)
concentration builds up in the thylakoid
p Part of non-cyclic photophosphorylation
–
§ Chemiosmosis- generates ATP
Chemiosmosis
Light independent
p Calvin
Cycle- Stroma of the chloroplast
Summary of Photosynthesis
Phosphorlation
= ADP + Pi ATP
l Photophosphorlation
¡ Generating ATP from the conversion of electromagnetic energy of a
photon.
l Oxidative
phosphorlation
¡Generating ATP from chemical
energy from a redox reactions of the electron
transport chain
l Substrate
phosphorlation
¡ATP generated via an
enzyme catalyzed reaction with an intermediate substrate
l Glycolysis and Krebs cycle
Metabolism – break down of food to make ATP
Animal Cell
Plant cell
C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O
Glycolysis
l Initial stage in the cytosol
of a cell
l Requires
2 ATP to start the reaction
l Glucose is oxidized to Pyruvic acid
l Net 2 ATP produced
l Also
NADPH
Krebs cycle
l products of glycolysis are further oxidized CO2 is produced
l 2
ATP produced more NADPH and FADH
Electron transport chain
l Inner membrane of the mitochondria
l A series of redox reactions transferring
an electron.
l The energy released is used to synthesize ATP 32 ATP
lBy chemiosmosis
What happens to the excess H+ and electrons?
l molecular oxygen is
the final electron acceptor
l Along with H +
ions and the final electrons, oxygen combine to form metabolic water